- A binary tree is a data structure where each node has two pointers, each pointing to another node or containing a
null value.
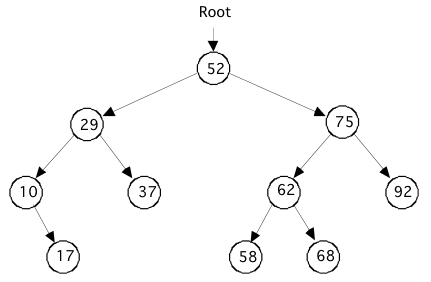
The following binary tree terms will be defined and applied to the above example.
-
Root node - the top node in the tree; the node whose value is 52.
-
Parent node - a node that points to one or two nodes below it.
-
Child node - the node being pointed to by a parent; every node in the tree is a child to another node, except for the root node.
-
Leaf - a node that has no children
-
Level - the distance from the root, calculated by counting the shortest distance from the root to that node. Examples: 29 is stored in a node at level 1, 62 is stored in a node at level 2, 17 is stored at level 3, etc.
-
Edge - an edge joins two nodes. In the above diagram, each arrow represents an edge.
-
This tree is an example of an ordered binary tree that has the following property. For every parent node, a child to the right will have a larger value, while a child to the left will have a smaller value.
-
A subtree is the entire left branch or right branch of a node. For example, the left subtree of the node containing 52 has 4 nodes. The right subtree of node containing 75 has only 1 node.
-
A leaf will have two null pointers.


